01 / Case Study
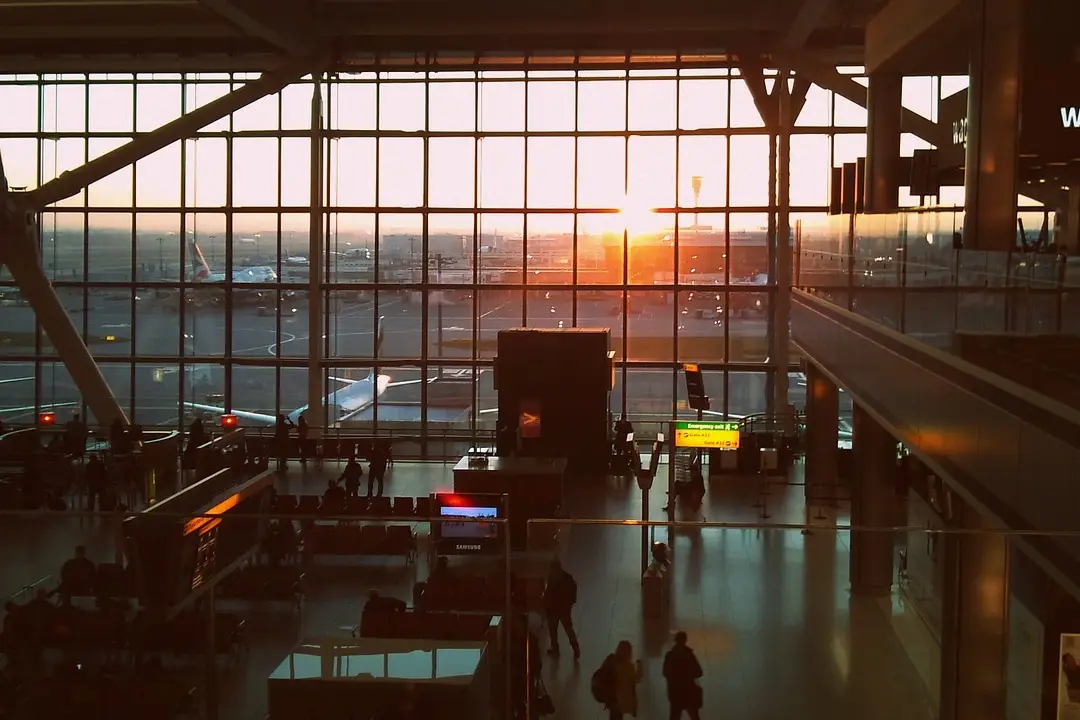
Heathrow Terminal 5C, London
DSSR designed all Mechanical and Electrical building services for Terminal 5C, interfacing with specialist airport systems.
© Header: James Z_Vancouver, Canada, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Location / Heathrow, London
Contract Value / £220m
Architect / Richard Rogers Partnership
Client / Carillion/HAL
Completion / 2011
02 / Overview
Overview of the Heathrow Terminal 5C project
T5C was constructed while the rest of Terminal 5 (T5) was in operation and was completed in early 2011. T5C is located airside, meaning it is situated within the secure area of the airport, and it serves as a facility for arrivals, departures, retail, and CIP (Commercially Important Passengers) areas, with baggage and transportation links to the existing T5 buildings.
© Terminal 5 Insider, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons / © Rossographer / Interior, Heathrow Terminal 5
The design of T5C included the provision of 12 gates, with flexibility for future expansion to 14 gates. This was done to accommodate potential growth and changes in airline operations. The gates were designed to be adaptable and flexible, allowing for efficient handling of passengers and aircraft movements.
Specialised interfaces
As part of the building services design, all mechanical, electrical, and public health systems were carefully integrated into T5C. These systems included heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) for maintaining comfortable indoor environments, power distribution for reliable electrical supply, and plumbing systems for potable water supply and waste management. In addition, T5C required specialised interfaces with specialist airport systems, such as baggage handling and security systems, to ensure smooth operations and efficient passenger flow.
Efficient utilisation of resources
The planning and infrastructure services for T5C were provided by the existing BAA (British Airports Authority) Terminal 5 district networks. This included chilled water, heating, power, potable water, and firefighting water, which were interconnected with the existing systems of Terminal 5. This allowed for the efficient utilisation of resources and integration with the overall infrastructure of the airport.